Add feature flags in SvelteKit apps with Neon Postgres
Step-by-step guide to integrating feature flags in SvelteKit apps with Postgres
This guide covers the step-by-step process of integrating feature flags in SvelteKit apps with Postgres (powered by Neon). Feature flags provide a way to control the behavior of your application without deploying new code, allowing you to test and roll out new features dynamically. Upon completing the guide, you would have an understanding of managing and rolling out of new features (such as a hypothetical faster payment method) using dynamic feature flags integration.
Prerequisites
To follow along this guide, you will need the following:
- Node.js 18 or later
- A Neon account – The feature flags will be defined (or mutated) in a Serverless Postgres
Steps
- Provisioning a Serverless Postgres powered by Neon
- Create a new SvelteKit application
- (Optional) Add Tailwind CSS to the application
- Managing Feature Flags in Serverless Postgres
- Dynamic Feature Flag Integration for Testing Fast Payment Methods
Provisioning a Serverless Postgres powered by Neon
Using Serverless Postgres database powered by Neon helps you scale down to zero. With Neon, you only have to pay for what you use.
To get started, go to the Neon console and enter the name of your choice as the project name.
You will then be presented with a dialog that provides a connecting string of your database. Click on Pooled connection on the top right of the dialog and the connecting string automatically updates in the box below it.
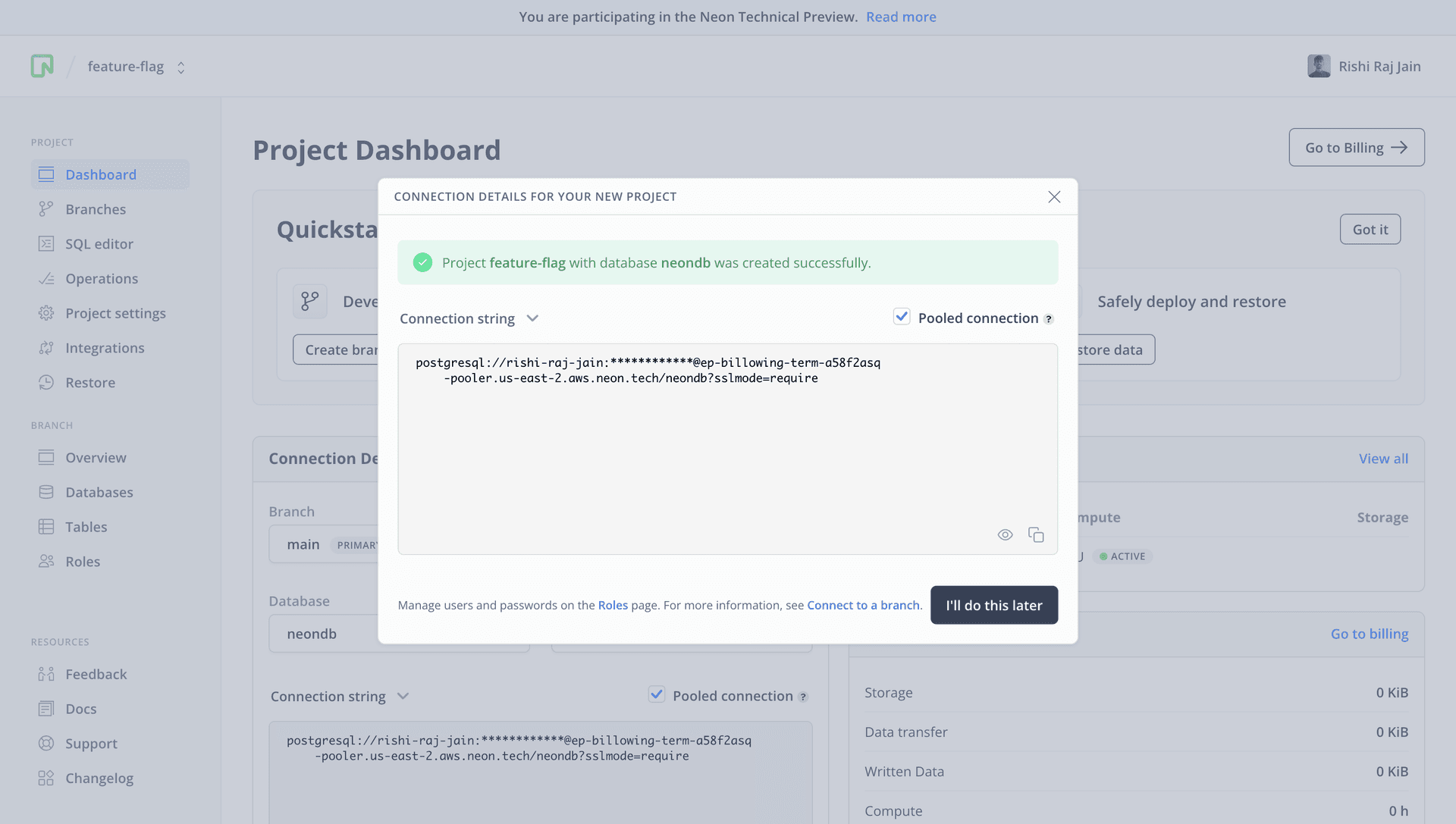
All Neon connection strings have the following format:
postgres://<user>:<password>@<endpoint_hostname>.neon.tech:<port>/<dbname>useris the database user.passwordis the database user’s password.endpoint_hostnameis the host with neon.tech as the TLD.portis the Neon port number. The default port number is 5432.dbnameis the name of the database. “neondb” is the default database created with each Neon project.?sslmode=requirean optional query parameter that enforces the SSL mode while connecting to the Postgres instance for better security.
Save this connecting string somewhere safe to be used as the DATABASE_URL further in the guide. Proceed further in this guide to create a SvelteKit application.
Create a new SvelteKit application
To start building the application, create a new SvelteKit project. Open your terminal and run the following command:
npm create svelte@latest my-appWhen prompted, choose:
Skeleton projectfor Which Svelte app template?Yes, using Typescript syntaxfor Add type checking with Typescript?
Press Enter to proceed. Now, follow the instructions to install the dependencies and start the development server:
npm run devThe app now should be running on localhost:5173.
Note: According to an advanced SvelteKit guide, using
.serverin the filename allows you to make it server-only.
Next, run the command below to install the necessary libraries and packages for building the application:
npm install pg
npm install -D dotenv tsx @types/pgIt installs the packages passed to the install command, with the -D flag specifying the libraries intended for development purposes only.
The libraries installed include:
pg: A PostgreSQL client for Node.js.
The development-specific libraries include:
@types/pg: Type definitions for pg.tsx: To execute and rebuild TypeScript efficiently.dotenv: A library for handling environment variables.
(Optional) Add Tailwind CSS to the application
For styling the app, we will be using Tailwind CSS. Install and set up Tailwind at the root of our project's directory by running:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
npx tailwindcss init -pCreate an app.css file in the src directory, and add the snippet below in it:
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;Next, add the paths to all of your template files in your tailwind.config.js file:
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
export default {
- content: [],
+ content: ['./src/**/*.{html,js,svelte,ts}'],
theme: {
extend: {}
},
plugins: []
};Finally, add an import to app.css in your +page.svelte file:
+ <script lang="ts">
+ import '../app.css'
+ </script>
<!-- +page.svelte's HTML -->Managing Feature Flags in Serverless Postgres
Feature flags offer a powerful way to control the behavior of your application without deploying new code. In a Serverless Postgres environment, you can easily create, read, and update feature flags using the following steps:
Create a Serverless Postgres Client
To create a client that interacts with your serverless postgres, create a postgres.server.ts file inside the src/lib directory with the following content:
// File: src/lib/postgres.server.ts
// Load the postgres module
import pg from 'pg'
// Load Environment Variables
import 'dotenv/config'
// Create a connection string to the Neon Postgres instance
const connectionString: string = process.env.DATABASE_URL as string
// Create a in-memory pool so that it's cached for multiple calls
export default new pg.Pool({ connectionString })The code above starts with importing the Postgres client. It further imports the config module by dotenv that makes sure that all environment variables are populated in application environment. It then creates a new instance of a PostgreSQL connection pool.
To create, read or update the feature flags from your SvelteKit application, you can use re-usable helper functions. Let's create a new directory by executing the following command in your terminal window to start creating those functions:
mkdir src/lib/feature_flagsCreate & Populate Feature Flags Database
In the feature_flags directory, create a file named setup.server.ts with the following code which will allow you to create and populate a database table for feature flags.
// File: src/lib/feature_flags/setup.server.ts
import pool from '../postgres.server'
async function populateFeatureFlags() {
await pool.query('CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS feature_flags (flagName text PRIMARY KEY, enabled boolean);')
console.log('✅ Setup database for feature flag')
await pool.query({
text: 'INSERT INTO feature_flags (flagName, enabled) VALUES ($1, $2)',
values: ['fast_payments', true],
})
console.log('✅ Setup an enabled feature flag to accept fast payment methods.')
}
populateFeatureFlags()The code snippet above first ensures the existence of a table named feature_flags in the PostgreSQL database. Then, it inserts a feature flag named fast_payments with the value true, indicating that fast payment methods are enabled.
READ and UPDATE the Feature Flags
In the feature_flags directory, create a file named get.server.ts with the following code which will allow you to read the feature flag value in the database.
// File: src/lib/feature_flags/get.server.ts
import pool from '../postgres.server'
export const isEnabled = async (flagName: string): Promise<boolean> => {
const { rows } = await pool.query({
text: 'SELECT enabled FROM feature_flags WHERE flagName = $1',
values: [flagName],
})
return rows[0].enabled
}The isEnabled function queries the database to check whether a specific feature flag is enabled or not. In this example, you will use it to check if fast_payments feature flag is enabled or not.
In the feature_flags directory, create a file named set.server.ts with the following code which will allow you to update the feature flag value in the database.
// File: src/lib/feature_flags/set.server.ts
import pool from '../postgres.server'
export const setEnabled = async (flagName: string, flagValue: boolean) => {
await pool.query({
text: 'UPDATE feature_flags SET enabled = $2 WHERE flagName = $1',
values: [flagName, flagValue],
})
}The setEnabled function updates the value of a feature flag in the database. In this example, you will update the fast_payments feature dynamically per request to get a taste of how feature flags are used in production.
Great! You can use these helper functions in your application to manage and control feature flags dynamically.
Dynamic Feature Flag Integration for Testing Fast Payment Methods
In this section, you will get an example of how feature flag helps test and roll out new features, dynamically. For example, you are a payment processing company. You have just added a payment method named PayGM that helps users pay faster. But you want to test it out on a random basis for each cart that you process. Let's walk through a hypothetical code that allows you to understand the usage of feature flag in this case.
Update Feature Flags Dynamically
In a SvelteKit route, the data from the server to the user interface is passed via +page.server.ts file to +page.svelte. For the sake of an example, you will update the feature flag dynamically and load it per request to check if it's enabled. To do that, add the following snippet to +page.server.ts file:
// File: src/routes/+page.server.ts
import { isEnabled } from '$lib/feature_flags/get.server'
import { setEnabled } from '$lib/feature_flags/set.server'
export async function load() {
await setEnabled('fast_payments', Math.random() > 0.5)
return {
fast_payments: await isEnabled('fast_payments'),
}
}The above code first updates the value of the feature flag in the database randomly as a boolean whenever the / route is visited. Finally, it fetches the feature flag value to check if the fast payment methods are enabled or not.
Creating a Conditional User Experience
Now, let's look at how the feature flag value can be used in the user interface to conditionally render UI elements. This will allow you to accept payments via PayGM if the fast_payments feature flag is enabled. To do that, use the following code in +page.svelte file:
<script lang="ts">
// File: src/routes/+page.svelte
import '../app.css'
import type { PageData } from './$types'
export let data: PageData
</script>
<div class="w-screen h-screen flex flex-col items-center justify-center">
{#if data.fast_payments}
<div class="mb-6 w-full flex flex-col max-w-[300px]">
<span class="font-semibold">Fast Payment Methods</span>
<button class="mt-3 flex flex-col items-center border rounded w-full px-3 py-1">Pay via PayGM</button>
</div>
{/if}
<form action="/" method="post" class="w-full flex flex-col max-w-[300px]">
<span class="font-semibold">Pay with card</span>
<input class="mt-3 w-full border px-2 py-1 rounded" type="text" placeholder="Full name on card" />
<input class="mt-3 w-full border px-2 py-1 rounded" type="text" placeholder="1234 1234 1234 1234" />
<div class="flex flex-row gap-x-2">
<input class="w-1/2 border px-2 py-1 rounded" type="text" placeholder="MM/YY" />
<input class="w-1/2 border px-2 py-1 rounded" type="text" placeholder="CVV" />
</div>
</form>
</div>In the code above, UI elements related to fast payment methods are conditionally rendered based on the value of the fast_payments feature flag. If fast_payments feature flag is enabled, the UI will display options for paying via PayGM; otherwise, it will display options for paying with a card.
Summary
In this guide, you learned how to add feature flags in your SvelteKit apps using Serverless Postgres powered by Neon. By dynamically updating and utilizing feature flags, you can effectively test and roll out new features like fast payment methods, providing a controlled and iterative approach to your deployments.
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. Users on paid plans can open a support ticket from the console. For more detail, see Getting Support.
Last updated on